Which of the following security architectures defines how to integrate widely disparate applications for a world that is Web-based and uses multiple implementation platforms?
A. Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture
B. Enterprise architecture
C. Service-oriented architecture
D. Service-oriented modeling and architecture
A. Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture
B. Enterprise architecture
C. Service-oriented architecture
D. Service-oriented modeling and architecture
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
Explanation: In computing, a service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a flexible set of design principles used during the phases of systems development and integration. A deployed SOA-based architecture will provide a loosely-integrated suite of services that can be used within multiple business domains. SOA also generally provides a way for consumers of services, such as web-based applications, to be aware of available SOA-based services. For example, several disparate departments within a company may develop and deploy SOA services in different implementation languages; their respective clients will benefit from a well understood, well defined interface to access them. XML is commonly used for interfacing with SOA services, though this is not required. SOA defines how to integrate widely disparate applications for a world that is Web-based and uses multiple implementation platforms. Rather than defining an API, SOA defines the interface in terms of protocols and functionality. An endpoint is the entry point for such an SOA implementation.
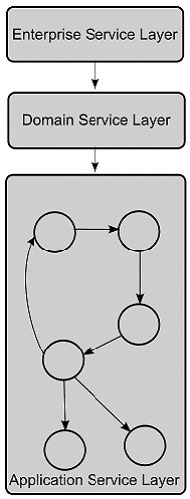
(Layer interaction in Service-oriented architecture) Answer: A is incorrect. SABSA (Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture) is a framework and methodology for Enterprise Security Architecture and Service Management. SABSA is a model and a methodology for developing risk-driven enterprise information security architectures and for delivering security infrastructure solutions that support critical business initiatives. The primary characteristic of the SABSA model is that everything must be derived from an analysis of the business requirements for security, especially those in which security has an enabling function through which new business opportunities can be developed and exploited. Answer: D is incorrect. The service-oriented modeling and architecture (SOMA) includes an analysis and design method that extends traditional object-oriented and component-based analysis and design methods to include concerns relevant to and supporting SOA. Answer: B is incorrect. Enterprise architecture describes the terminology, the composition of subsystems, and their relationships with the external environment, and the guiding principles for the design and evolution of an enterprise.

(Layer interaction in Service-oriented architecture) Answer: A is incorrect. SABSA (Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture) is a framework and methodology for Enterprise Security Architecture and Service Management. SABSA is a model and a methodology for developing risk-driven enterprise information security architectures and for delivering security infrastructure solutions that support critical business initiatives. The primary characteristic of the SABSA model is that everything must be derived from an analysis of the business requirements for security, especially those in which security has an enabling function through which new business opportunities can be developed and exploited. Answer: D is incorrect. The service-oriented modeling and architecture (SOMA) includes an analysis and design method that extends traditional object-oriented and component-based analysis and design methods to include concerns relevant to and supporting SOA. Answer: B is incorrect. Enterprise architecture describes the terminology, the composition of subsystems, and their relationships with the external environment, and the guiding principles for the design and evolution of an enterprise.