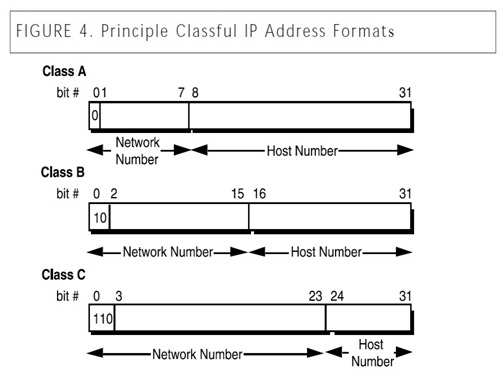
Each Class B network address has a 16-bit network prefix, with the two highest order bits set to 1-0. The following answers are incorrect: The first bit of the IP address would be set to zero. Is incorrect because, this would be a Class A network address. The first two bits of the IP address would be set to one, and the third bit set to zero. Is incorrect because, this would be a Class
C network address.
The first three bits of the IP address would be set to one. Is incorrect because, this is a distractor. Class D & E have the first three bits set to 1. Class D the 4th bit is 0 and for Class E the 4th bit to 1. Classless Internet Domain Routing (CIDR)
High Order bits are shown in bold below.
For Class A, the addresses are 0.0.0.0 -127.255.255.255
The lowest Class A address is represented in binary as 00000000.00000000.0000000.00000000
For Class B networks, the addresses are 128.0.0.0 -191.255.255.255.
The lowest Class B address is represented in binary as 10000000.00000000.00000000.00000000
For Class C, the addresses are 192.0.0.0 -223.255.255.255
The lowest Class C address is represented in binary as 11000000.00000000.00000000.00000000
For Class D, the addresses are 224.0.0.0 -239.255.255.255 (Multicast)
The lowest Class D address is represented in binary as 11100000.00000000.00000000.00000000
For Class E, the addresses are 240.0.0.0 -255.255.255.255 (Reserved for future usage)
The lowest Class E address is represented in binary as 11110000.00000000.00000000.00000000 Classful IP Address Format
References: 3Com
http://www.3com.com/other/pdfs/infra/corpinfo/en_US/501302.pdf AIOv3 Telecommunications and Networking Security (page 438)
