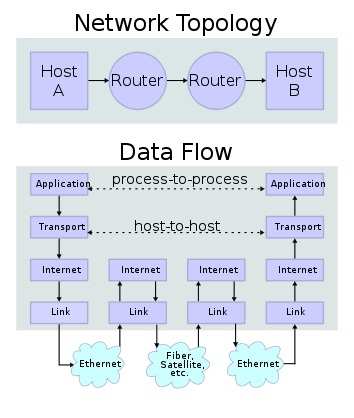
TCP is a reliable connection-oriented transport for guaranteed delivery of data.
Protocols represent certain rules and regulations that are essential in order to have data communication between two entities. Internet Protocols work in sending and receiving data packets. This type of communication may be either connection-less or connection-oriented.
In a connection-oriented scenario, an acknowledgement is being received by the sender from the receiver in support of a perfect transfer. Transmission Control Protocol or TCP is such a protocol.
On the other hand, UDP or User Datagram Protocol is of the connection-less type where no feedback is being forwarded to the sender after delivery and the data transfer have taken place or not. Though, it’s not a guaranteed method, but, once a connection is established, UDP works much faster than TCP as TCP has to rely on a feedback and accordingly, the entire 3way handshaking takes place.
The following answers are incorrect:
UDP provides for Error Correction, TCP does not: UDP does not provide for error correction, while TCP does.
UDP is useful for longer messages, rather than TCP: UDP is useful for shorter messages due to its connectionless nature. TCP does not guarantee delivery of data, while UDP does guarantee data delivery: The opposite is true.
References Used for this question:
http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/key-differences-between-tcp-and-udp-pr… http://www.skullbox.net/tcpudp.php James’s TCP-IP FAQ -Understanding Port Numbers.