When we encrypt messages using our private keys which are only available to us. The person who wants to read and decrypt the message need only have our public keys to do so. The whole point to PKI is to assure message integrity, authentication of the source, and to provide secrecy with the digital encryption.
See below a nice walktrough of Digital Signature creation and verification from the Comodo web site:
Digital Signatures apply the same functionality to an e-mail message or data file that a handwritten signature does for a paper-based document. The Digital Signature vouches for the origin and integrity of a message, document or other data file. How do we create a Digital Signature?
The creation of a Digital Signature is a complex mathematical process. However as the complexities of the process are computed by the computer, applying a Digital Signature is no more difficult that creating a handwritten one!
The following text illustrates in general terms the processes behind the generation of a Digital Signature:
1. Alice clicks ‘sign’ in her email application or selects which file is to be signed.
2. Alice’s computer calculates the ‘hash’ (the message is applied to a publicly known mathematical hashing function that coverts the message into a long number referred to as the hash).
3. The hash is encrypted with Alice’s Private Key (in this case it is known as the Signing Key) to create the Digital Signature.
4. The original message and its Digital Signature are transmitted to Bob.
5. Bob receives the signed message. It is identified as being signed, so his email application knows which actions need to be performed to verify it.
6. Bob’s computer decrypts the Digital Signature using Alice’s Public Key.
7. Bob’s computer also calculates the hash of the original message (remember -the mathematical function used by Alice to do this is publicly known).
8. Bob’s computer compares the hashes it has computed from the received message with the now decrypted hash received with Alice’s message.
digital signature creation and verification
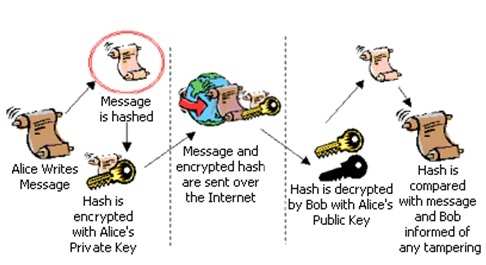
If the message has remained integral during its transit (i.e. it has not been tampered with), when compared the two hashes will be identical.
However, if the two hashes differ when compared then the integrity of the original message has been compromised. If the original message is tampered with it will result in Bob’s computer calculating a different hash value. If a different hash value is created, then the original message will have been altered. As a result the verification of the Digital Signature will fail and Bob will be informed. Origin, Integrity, Non-Repudiation, and Preventing Men-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks
Eve, who wants to impersonate Alice, cannot generate the same signature as Alice because she does not have Alice’s Private Key (needed to sign the message digest). If instead, Eve decides to alter the content of the message while in transit, the tampered message will create a different message digest to the original message, and Bob’s computer will be able to detect that. Additionally, Alice cannot deny sending the message as it has been signed using her Private Key, thus ensuring non-repudiation.
creating and validating a digital signature
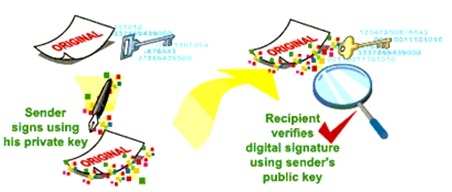
Due to the recent Global adoption of Digital Signature law, Alice may now sign a transaction, message or piece of digital data, and so long as it is verified successfully it is a legally permissible means of proof that Alice has made the transaction or written the message.
The following answers are incorrect:
-Public / Private: This is the opposite of the right answer.
-Symmetric / Asymmetric: Not quite. Sorry. This form of crypto is asymmetric so you were almost on target.
-Private / Symmetric: Well, you got half of it right but Symmetric is wrong.
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
The CCCure Holistic Security+ CBT, you can subscribe at:
http://www.cccure.tv and
http://www.comodo.com/resources/small-business/digital-certificates…


