While a digital signature binds a document to the possessor of a particular key, a digital timestamp binds a document to its creation at a particular time.
Trusted timestamping is the process of securely keeping track of the creation and modification time of a document. Security here means that no one — not even the owner of the document — should be able to change it once it has been recorded provided that the timestamper’s integrity is never compromised.
The administrative aspect involves setting up a publicly available, trusted timestamp management infrastructure to collect, process and renew timestamps or to make use of a commercially available time stamping service.
A modern example of using a Digital Timestamp is the case of an industrial research organization that may later need to prove, for patent purposes, that they made a particular discovery on a particular date; since magnetic media can be altered easily, this may be a nontrivial issue. One possible solution is for a researcher to compute and record in a hardcopy laboratory notebook a cryptographic hash of the relevant data file. In the future, should there be a need to prove the version of this file retrieved from a backup tape has not been altered, the hash function could be recomputed and compared with the hash value recorded in that paper notebook.
According to the RFC 3161 standard, a trusted timestamp is a timestamp issued by a trusted third party (TTP) acting as a Time Stamping Authority (TSA). It is used to prove the existence of certain data before a certain point (e.g. contracts, research data, medical records,…) without the possibility that the owner can backdate the timestamps. Multiple TSAs can be used to increase reliability and reduce vulnerability.
The newer ANSI ASC X9.95 Standard for trusted timestamps augments the RFC 3161 standard with data-level security requirements to ensure data integrity against a reliable time source that is provable to any third party. This standard has been applied to authenticating digitally signed data for regulatory compliance, financial transactions, and legal evidence.
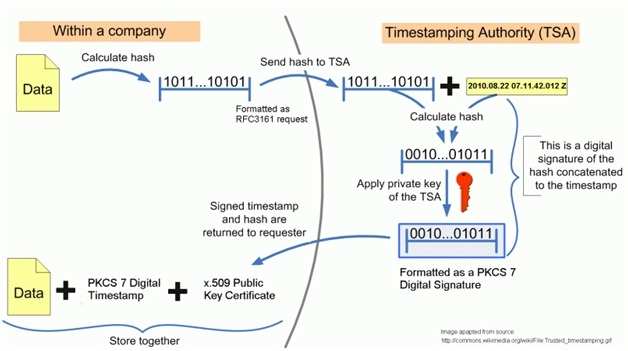
Digital TimeStamp
The following are incorrect answers:
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is used to achieve high accuracy time synchronization for computers across a network. A Certification Authority (CA) is the entity responsible for the issuance of digital certificates. A Digital Signature provides integrity and authentication but does not bind a document to a specific time it was created.
Reference used for this question:
http://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Trusted_timestamping.gif and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trusted_timestamping