How many bits of a MAC address uniquely identify a vendor, as provided by the IEEE?
A. 6 bits
B. 12 bits
C. 16 bits
D. 24 bits
A. 6 bits
B. 12 bits
C. 16 bits
D. 24 bits
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
The MAC address is 48 bits long, 24 of which identify the vendor, as provided by the IEEE. The other 24 bits are provided by the vendor.
A media access control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. MAC addresses are used for numerous network technologies and most IEEE 802 network technologies, including Ethernet. Logically, MAC addresses are used in the media access control protocol sublayer of the OSI reference model.
MAC addresses are most often assigned by the manufacturer of a network interface card (NIC) and are stored in its hardware, such as the card’s read-only memory or some other firmware mechanism. If assigned by the manufacturer, a MAC address usually encodes the manufacturer’s registered identification number and may be referred to as the burned-in address. It may also be known as an Ethernet hardware address (EHA), hardware address or physical address. This is can be contrasted to a programmed address, where the host device issues commands to the NIC to use an arbitrary address. An example is many SOHO routers, where the ISP grants access to only one MAC address (used previously to inserting the router) so the router must use that MAC address on its Internet-facing NIC. Therefore the router administrator configures a MAC address to override the burned-in one.
A network node may have multiple NICs and each must have one unique MAC address per NIC.
See diagram below from Wikipedia showing the format of a MAC address. :
MAC Address format
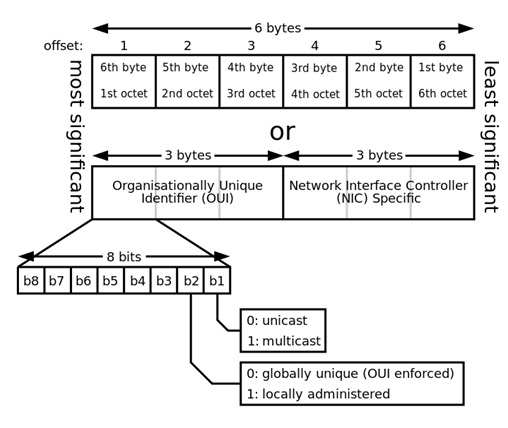
Reference(s) used for this question: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAC_address
A media access control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. MAC addresses are used for numerous network technologies and most IEEE 802 network technologies, including Ethernet. Logically, MAC addresses are used in the media access control protocol sublayer of the OSI reference model.
MAC addresses are most often assigned by the manufacturer of a network interface card (NIC) and are stored in its hardware, such as the card’s read-only memory or some other firmware mechanism. If assigned by the manufacturer, a MAC address usually encodes the manufacturer’s registered identification number and may be referred to as the burned-in address. It may also be known as an Ethernet hardware address (EHA), hardware address or physical address. This is can be contrasted to a programmed address, where the host device issues commands to the NIC to use an arbitrary address. An example is many SOHO routers, where the ISP grants access to only one MAC address (used previously to inserting the router) so the router must use that MAC address on its Internet-facing NIC. Therefore the router administrator configures a MAC address to override the burned-in one.
A network node may have multiple NICs and each must have one unique MAC address per NIC.
See diagram below from Wikipedia showing the format of a MAC address. :
MAC Address format

Reference(s) used for this question: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAC_address