A large mobile network operating company is building a machine learning model to predict customers who are likely to unsubscribe from the service. The company plans to offer an incentive for these customers as the cost of churn is far greater than the cost of the incentive.
The model produces the following confusion matrix after evaluating on a test dataset of 100 customers:
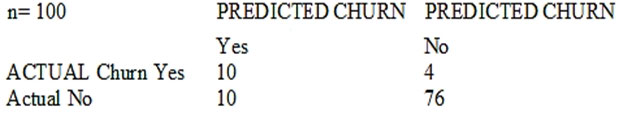
Based on the model evaluation results, why is this a viable model for production?
A. The model is 86% accurate and the cost incurred by the company as a result of false negatives is less than the false positives.
B. The precision of the model is 86%, which is less than the accuracy of the model.
C. The model is 86% accurate and the cost incurred by the company as a result of false positives is less than the false negatives.
D. The precision of the model is 86%, which is greater than the accuracy of the model.
The model produces the following confusion matrix after evaluating on a test dataset of 100 customers:
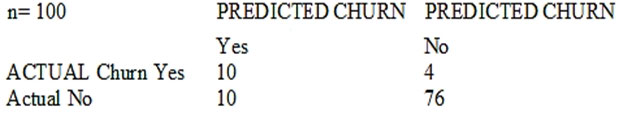
Based on the model evaluation results, why is this a viable model for production?
A. The model is 86% accurate and the cost incurred by the company as a result of false negatives is less than the false positives.
B. The precision of the model is 86%, which is less than the accuracy of the model.
C. The model is 86% accurate and the cost incurred by the company as a result of false positives is less than the false negatives.
D. The precision of the model is 86%, which is greater than the accuracy of the model.