A data scientist is training a text classification model by using the Amazon SageMaker built-in BlazingText algorithm. There are 5 classes in the dataset, with 300 samples for category A, 292 samples for category B, 240 samples for category C, 258 samples for category D, and 310 samples for category E.
The data scientist shuffles the data and splits off 10% for testing. After training the model, the data scientist generates confusion matrices for the training and test sets.
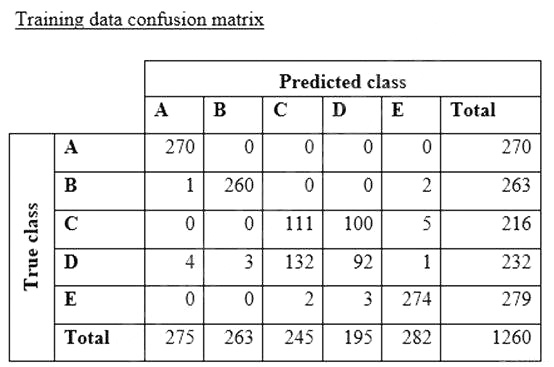
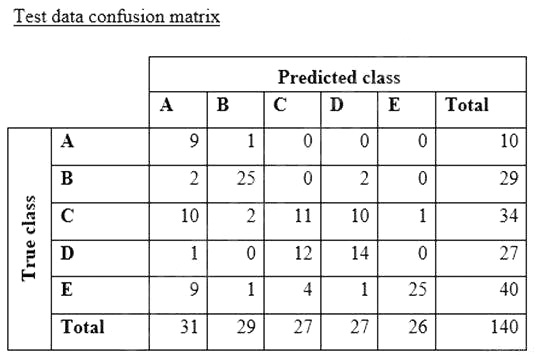
What could the data scientist conclude form these results?
A. Classes C and D are too similar.
B. The dataset is too small for holdout cross-validation.
C. The data distribution is skewed.
D. The model is overfitting for classes B and E.
The data scientist shuffles the data and splits off 10% for testing. After training the model, the data scientist generates confusion matrices for the training and test sets.


What could the data scientist conclude form these results?
A. Classes C and D are too similar.
B. The dataset is too small for holdout cross-validation.
C. The data distribution is skewed.
D. The model is overfitting for classes B and E.