Explanation: ElastiCache for Memcached The primary goal of caching is typically to offload reads from your database or other primary data source. In most apps, you have hot spots of data that are regularly queried, but only updated periodically. Think of the front page of a blog or news site, or the top 100 leaderboard in an online game. In this type of case, your app can receive dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of requests for the same data before it’s updated again. Having your caching layer handle these queries has several advantages. First, it’s considerably cheaper to add an in-memory cache than to scale up to a larger database cluster. Second, an in-memory cache is also easier to scale out, because it’s easier to distribute an in-memory cache horizontally than a relational database. Last, a caching layer provides a request buffer in the event of a sudden spike in usage. If your app or game ends up on the front page of Reddit or the App Store, it’s not unheard of to see a spike that is 10 to 100 times your normal application load. Even if you autoscale your application instances, a 10x request spike will likely make your database very unhappy. Let’s focus on ElastiCache for Memcached first, because it is the best fit for a cachingfocused solution. We’ll revisit Redis later in the paper, and weigh its advantages and disadvantages. Architecture with ElastiCache for Memcached When you deploy an ElastiCache Memcached cluster, it sits in your application as a separate tier alongside your database. As mentioned previously, Amazon ElastiCache does not directly communicate with your database tier, or indeed have any particular knowledge of your database.
A simplified deployment for a web application looks something like this:
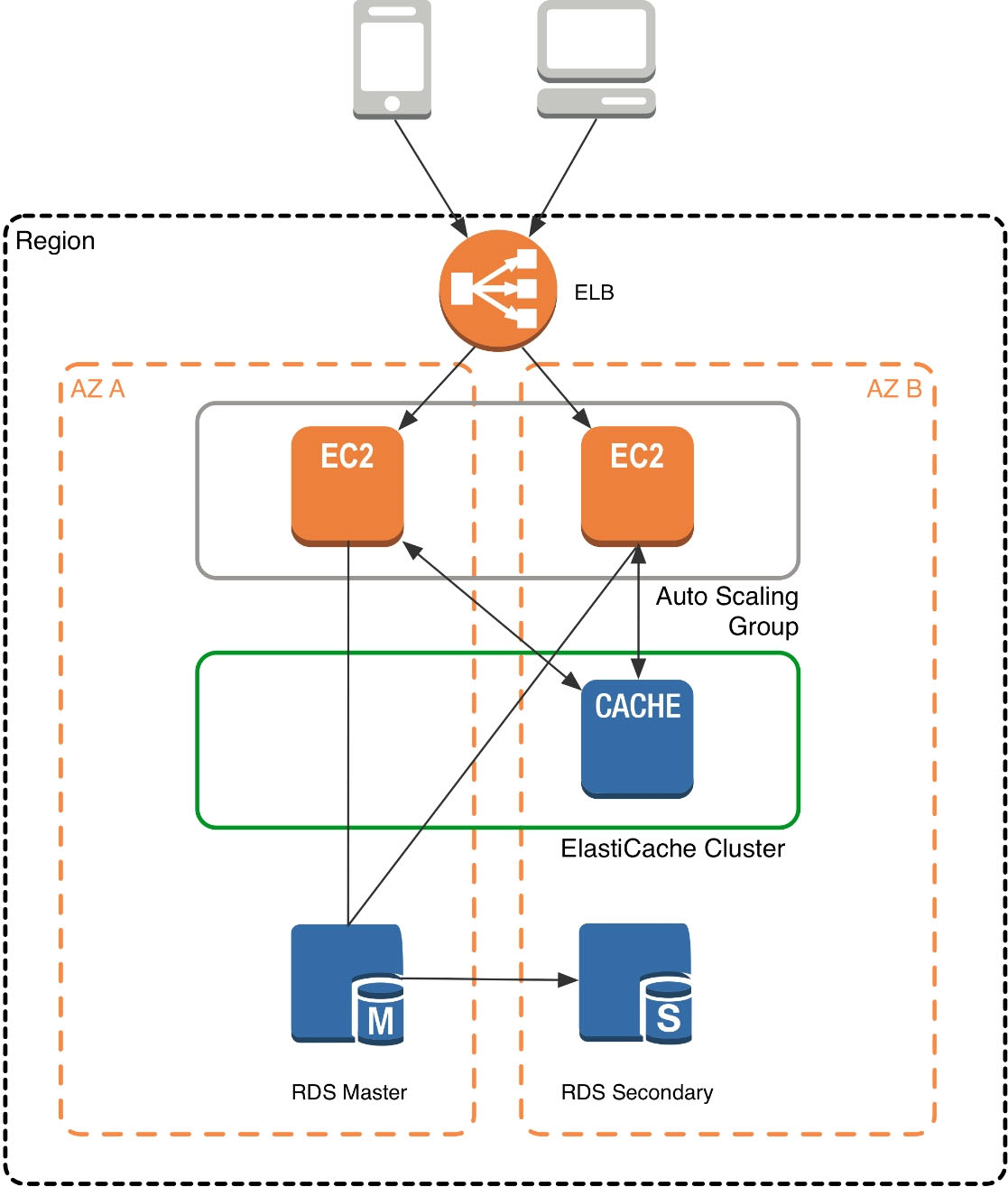
In this architecture diagram, the Amazon EC2 application instances are in an Auto Scaling group, located behind a load balancer using Elastic Load Balancing, which distributes requests among the instances. As requests come into a given EC2 instance, that EC2 instance is responsible for communicating with ElastiCache and the database tier. For development purposes, you can begin with a single ElastiCache node to test your application, and then scale to additional cluster nodes by modifying the ElastiCache cluster. As you add additional cache nodes, the EC2 application instances are able to distribute cache keys across multiple ElastiCache nodes. The most common practice is to use client-side sharding to distribute keys across cache nodes, which we will discuss later in this paper.
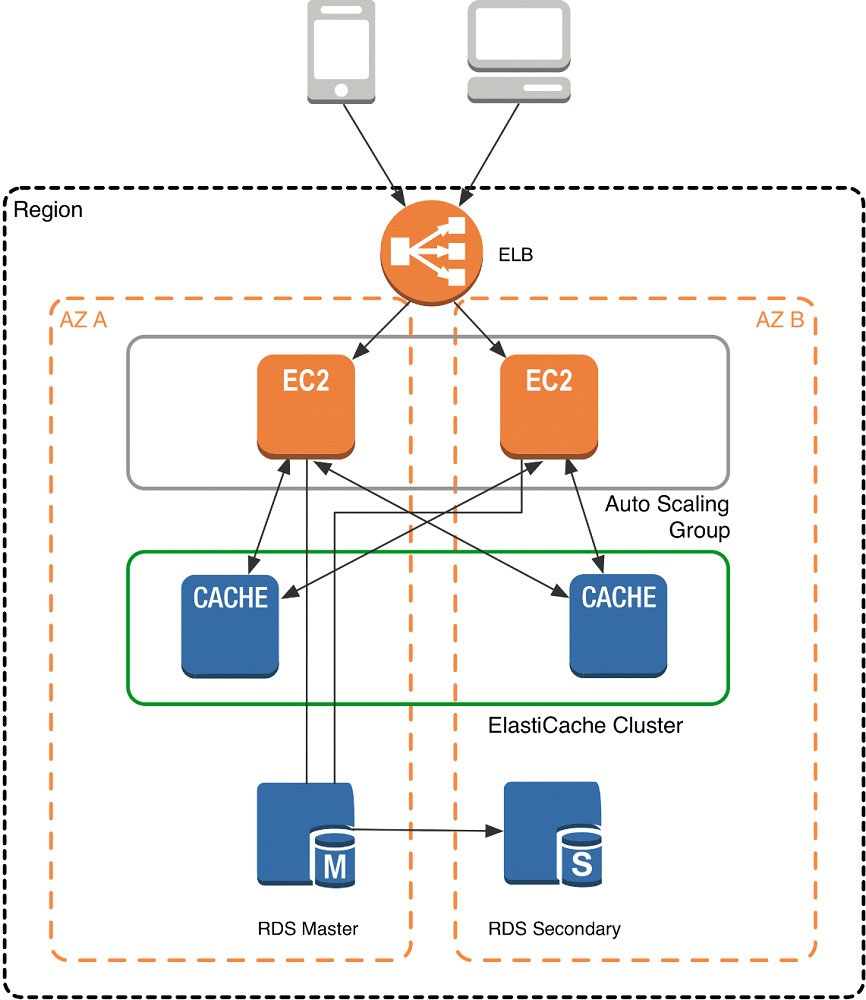
When you launch an ElastiCache cluster, you can choose the Availability Zone(s) that the cluster lives in. For best performance, you should configure your cluster to use the same Availability Zones as your application servers. To launch an ElastiCache cluster in a specific Availability Zone, make sure to specify the Preferred Zone(s) option during cache cluster creation. The Availability Zones that you specify will be where ElastiCache will launch your cache nodes. We recommend that you select Spread Nodes Across Zones, which tells ElastiCache to distribute cache nodes across these zones as evenly as possible. This distribution will mitigate the impact of an Availability Zone disruption on your ElastiCache nodes. The trade-off is that some of the requests from your application to ElastiCache will go to a node in a different Availability Zone, meaning latency will be slightly higher. For more details, refer to Creating a Cache Cluster in the Amazon ElastiCache User Guide. As mentioned at the outset, ElastiCache can be coupled with a wide variety of databases. Here is an example architecture that uses Amazon DynamoDB instead of Amazon RDS and MySQL:
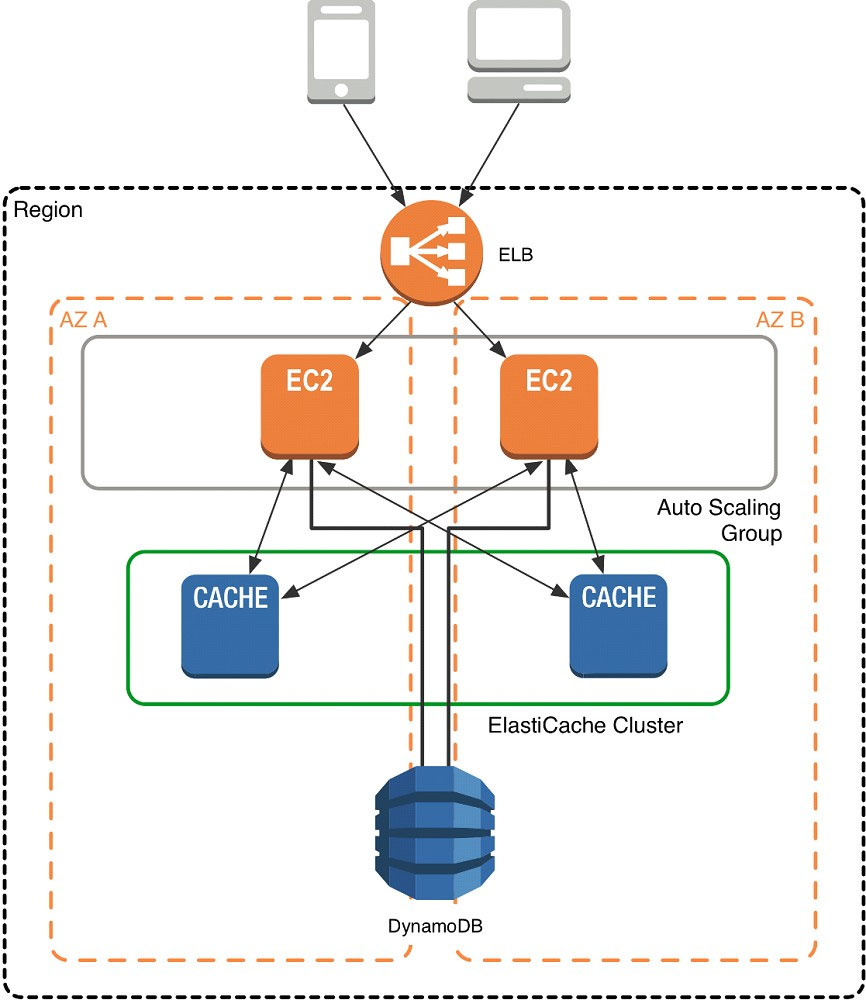
This combination of DynamoDB and ElastiCache is very popular with mobile and game companies, because DynamoDB allows for higher write throughput at lower cost than traditional relational databases. In addition, DynamoDB uses a key-value access pattern similar to ElastiCache, which also simplifies the programming model. Instead of using relational SQL for the primary database but then key-value patterns for the cache, both the primary database and cache can be programmed similarly. In this architecture pattern, DynamoDB remains the source of truth for data, but application reads are offloaded to ElastiCache for a speed boost.


