Explanation: AWS Direct Connect AWS Direct Connect makes it easy to establish a dedicated network connection from your premises to AWS. Using AWS Direct Connect, you can establish private connectivity between AWS and your datacenter, office, or collocation environment, which in many cases can reduce your network costs, increase bandwidth throughput, and provide a more consistent network experience than Internet-based connections. AWS Direct Connect lets you establish a dedicated network connection between your network and one of the AWS Direct Connect locations.
Using industry standard 802.1q VLANs, this dedicated connection can be partitioned into multiple virtual interfaces. This allows you to use the same connection to access public resources such as objects stored in Amazon S3 using public IP address space, and private resources such as Amazon EC2 instances running within an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) using private IP space, while maintaining network separation between the public and private environments.
Virtual interfaces can be reconfigured at any time to meet your changing needs. What is AWS Direct Connect? AWS Direct Connect links your internal network to an AWS Direct Connect location over a standard 1 gigabit or 10 gigabit Ethernet fiber-optic cable. One end of the cable is connected to your router, the other to an AWS Direct Connect router. With this connection in place, you can create virtual interfaces directly to the AWS cloud (for example, to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) and Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and to Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), bypassing Internet service providers in your network path. An AWS Direct Connect location provides access to Amazon Web Services in the region it is associated with, as well as access to other US regions.
For example, you can provision a single connection to any AWS Direct Connect location in the US and use it to access public AWS services in all US Regions and AWS GovCloud (US).
The following diagram shows how AWS Direct Connect interfaces with your network.
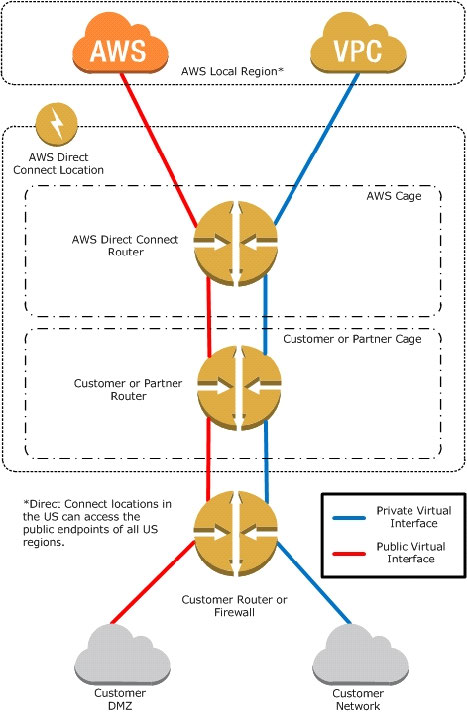
Requirements
To use AWS Direct Connect, your network must meet one of the following conditions: Your network is collocated with an existing AWS Direct Connect location. For more information on available AWS Direct Connect locations, go to
http://aws.amazon.com/directconnect/. You are working with an AWS Direct Connect partner who is a member of the AWS Partner Network (APN). For a list of AWS Direct Connect partners who can help you connect, go to
http://aws.amazon.com/directconnect. You are working with an independent service provider to connect to AWS Direct Connect. In addition, your network must meet the following conditions: Connections to AWS Direct Connect require single mode fiber, 1000BASE-LX (1310nm) for 1 gigabit Ethernet, or 10GBASELR (1310nm) for 10 gigabit Ethernet. Auto Negotiation for the port must be disabled. You must support 802.1Q VLANs across these connections. Your network must support Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and BGP MD5 authentication. Optionally, you may configure Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD).
To connect to Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), you must first do the following: Provide a private Autonomous System Number (ASN). Amazon allocates a private IP address in the 169.x.x.x range to you. Create a virtual private gateway and attach it to your VPC. For more information about creating a virtual private gateway, see Adding a Hardware Virtual Private Gateway to Your VPC in the Amazon VPC User Guide.
To connect to public AWS products such as Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3, you need to provide the following:
A public ASN that you own (preferred) or a private ASN. Public IP addresses (/31) (that is, one for each end of the BGP session) for each BGP session. If you do not have public IP
addresses to assign to this connection, log on to AWS and then open a ticket with AWS Support. The public routes that you will advertise over BGP.
