Explanation: Web Identity Federation Imagine that you are creating a mobile app that accesses AWS resources, such as a game that runs on a mobile device and stores player and score information using Amazon S3 and DynamoDB. When you write such an app, you’ll make requests to AWS services that must be signed with an AWS access key. However, we strongly recommend that you do not embed or distribute long-term AWS credentials with apps that a user downloads to a device, even in an encrypted store. Instead, build your app so that it requests temporary AWS security credentials dynamically when needed using web identity federation. The supplied temporary credentials map to an AWS role that has only the permissions needed to perform the tasks required by the mobile app. With web identity federation, you don’t need to create custom sign-in code or manage your own user identities. Instead, users of your app can sign in using a well-known identity provider (IdP) —such as Login with Amazon, Facebook, Google, or any other OpenID Connect (OIDC)-compatible IdP, receive an authentication token, and then exchange that token for temporary security credentials in AWS that map to an IAM role with permissions to use the resources in your AWS account. Using an IdP helps you keep your AWS account secure, because you don’t have to embed and distribute long-term security credentials with your application.
For most scenarios, we recommend that you use Amazon Cognito because it acts as an identity broker and does much of the federation work for you. For details, see the following section, Using Amazon Cognito for Mobile Apps. If you don’t use Amazon Cognito, then you must write code that interacts with a web IdP (Login with Amazon, Facebook, Google, or any other OIDC-compatible IdP) and then calls the AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity API to trade the authentication token you get from those IdPs for AWS temporary security credentials. If you have already used this approach for existing apps, you can continue to use it.
Using Amazon Cognito for Mobile Apps The preferred way to use web identity federation is to use Amazon Cognito. For example, Adele the developer is building a game for a mobile device where user data such as scores and profiles is stored in Amazon S3 and Amazon DynamoDB. Adele could also store this data locally on the device and use Amazon Cognito to keep it synchronized across devices. She knows that for security and maintenance reasons, long-term AWS security credentials should not be distributed with the game. She also knows that the game might have a large number of users. For all of these reasons, she does not want to create new user identities in IAM for each player.
Instead, she builds the game so that users can sign in using an identity that they’ve already established with a well-known identity provider, such as Login with Amazon, Facebook, Google, or any OpenID Connect (OIDC)-compatible identity provider. Her game can take advantage of the authentication mechanism from one of these providers to validate the user’s identity. To enable the mobile app to access her AWS resources, Adele first registers for a developer ID with her chosen IdPs.
She also configures the application with each of these providers. In her AWS account that contains the Amazon S3 bucket and DynamoDB table for the game, Adele uses Amazon Cognito to create IAM roles that precisely define permissions that the game needs. If she is using an OIDC IdP, she also creates an IAM OIDC identity provider entity to establish trust between her AWS account and the IdP. In the app’s code, Adele calls the sign-in interface for the IdP that she configured previously.
The IdP handles all the details of letting the user sign in, and the app gets an OAuth access token or OIDC ID token from the provider. Adele’s app can trade this authentication information for a set of temporary security credentials that consist of an AWS access key ID, a secret access key, and a session token. The app can then use these credentials to access web services offered by AWS. The app is limited to the permissions that are defined in the role that it assumes. The following figure shows a simplified flow for how this might work, using Login with Amazon as the IdP. For Step 2, the app can also use Facebook, Google, or any OIDC-compatible identity provider, but that’s not shown here. Sample workflow using Amazon Cognito to federate users for a mobile application
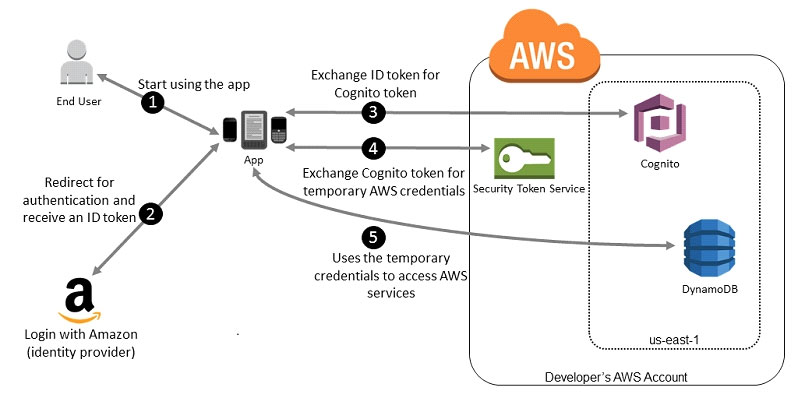
A customer starts your app on a mobile device. The app asks the user to sign in. The app uses Login with Amazon resources to accept the user’s credentials. The app uses Cognito APIs to exchange the Login with Amazon ID token for a Cognito token. The app requests temporary security credentials from AWS STS, passing the Cognito token. The temporary security credentials can be used by the app to access any AWS resources required by the app to operate. The role associated with the temporary security credentials and its assigned policies determines what can be accessed. Use the following process to configure your app to use Amazon Cognito to authenticate users and give your app access to AWS resources. For specific steps to accomplish this scenario, consult the documentation for Amazon Cognito. (Optional) Sign up as a developer with Login with Amazon, Facebook, Google, or any other OpenID Connect (OIDC)– compatible identity provider and configure one or more apps with the provider. This step is optional because Amazon Cognito also supports unauthenticated (guest) access for your users. Go to Amazon Cognito in the AWS Management Console. Use the Amazon Cognito wizard to create an identity pool, which is a container that Amazon Cognito uses to keep end user identities organized for your apps.
You can share identity pools between apps. When you set up an identity pool, Amazon Cognito creates one or two IAM roles (one for authenticated identities, and one for unauthenticated “guest” identities) that define permissions for Amazon Cognito users. Download and integrate the AWS SDK for iOS or the AWS SDK for Android with your app, and import the files required to use Amazon Cognito. Create an instance of the Amazon Cognito credentials provider, passing the identity pool ID, your AWS account number, and the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the roles that you associated with the identity pool.
The Amazon Cognito wizard in the AWS Management Console provides sample code to help you get started. When your app accesses an AWS resource, pass the credentials provider instance to the client object, which passes temporary security credentials to the client. The permissions for the credentials are based on the role or roles that you defined earlier.